-
What is Smart Packaging.

The importance of correct packaging
Each product shipped along domestic and international supply chain lines has its natural flow from beginning to end. Packaging is an essential element that manifests its presence within all stages of the product flow. Improving the whole supply chain from end to end relies on improved logistics and direct distribution processes.
These stages can be identified as the purchase of raw materials, the production and sale of the final product, and not to forget transportation, packaging, and distribution resources. Global ecommerce and online shipping services have become more influential than ever before. This critical piece of the supply chain cannot be ignored.
Packaging logistics is quite a new discipline that has gained consideration in terms of its strategic aspect in providing a significant competitive advantage to improve the efficiency of the direct distribution and internal supply chain logistics and shipping process.
Over the years, packaging has become a significant challenge for companies. Companies must analyze and study the best way to pack products taking into consideration many vital factors.
The characteristics of the products, such as the shape, components, etc., must be taken into account to minimize cost and improve the companies’ performance and reliability. As a result, the emphasis on packaging systems has grown substantially recently (Regattieri, 2013). This is true for traditional distribution and shipping as well as cross-border e-commerce solutions.
Whether a company specializes in local retail shipping and distribution, a solely online shot front, a hybrid blend of online and brick and mortar, or is looking at selling internationally on Shopify and similar Shopify markets, or a similar online platform, it all comes down to making smart choices at this critical point.
The Importance of Correct Packaging and Distribution Resources
Traditional packaging and distribution methods are insufficient to meet shifting market needs and changing consumer expectations. Working with local distribution providers as well as international domains and providers makes packaging all the more essential.
Understanding the different types of smart packaging available can set struggling companies apart from successful ones. Digital businesses, brick-and-mortar shops, online stores, and M-commerce solutions all benefit from this innovation.
Smart packaging consists of packaging systems with embedded sensor technology used for different product tracking. Direct distribution aims to extend its shelf life, track and trace products, monitor freshness, display information on quality, or improve the effect on customer safety.
Smart packaging contributes to the overall supply chain efficiency by constantly contacting the products through strategic sensors devices on the packaging. Smart packaging is integrated into products such as food, pharmaceutical, and many more. The Supply Chain packaging and distribution resource management are currently in a growth phase with immense potential.
New innovations with digitalization and automation, such as thin-film electronic and antimicrobial packing, are being analyzed to increase their capabilities and become even more accurate and safer (Cheung, 2018). It all comes down to improving supply chain management processes from end to end.
The three main Packaging levels and Direct Distribution
The packaging process consists of three primary levels. The first level is about the structural nature of the package. This phase is the smallest. Within this phase, the package is in direct contact with the actual content.
The second level deals with visual communication and customer satisfaction. The primary purpose of the second level is to keep packages in que and to follow their progress. It is a critical piece of the direct distribution puzzle.
Finally, the third level is designed and used for transportation and storage, such as cartons. The packaging system is cross-functional, which means that different departments dealing with the system each have specific requests about the design of the package.
The three package levels involved in packaging and distribution resource management are illustrated in the schema below.
The three package levels are illustrated in the schema below.
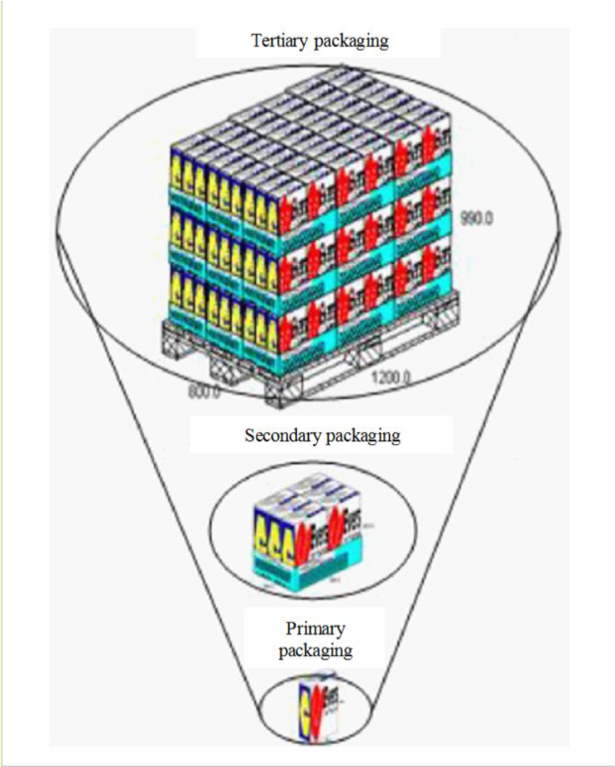
(Regattieri, 2013).
Smart Packaging Improves Security and Delivery Success
The security of the products can be monitored by research design to increase the safety of the product during manufacturing and assembly, storage and picking, and transport. Smart packaging also plays an important role in traditional packaging. Information transmission is used to inform the management team on the correct way to store or transport the contained product. Organizations also integrate the internet of things (IoT) through an electronic device RFDI (radio-frequency identification) which is a tag on packages to enable companies to identify the products in real-time, reducing the risk of damages and mapping the path of the products to control the work in progress. An unprotected product could cause product waste which can be negative from an environmental and economic point of view (Regattieri, 2013).

Shipper and Carrier Benefits to Smart Packaging
Smart Packaging can offer various advantages. They can fulfill the information, automation, marketing, and protective functions.
To accomplish this, packages are equipped with tiny electronic devices that add functionalities such as barcodes, LED, augmented reality, NFC (near field communication), loudspeakers, and displays.
A good example would be intelligent drug packaging with built-in RFID (radio frequency identification) chips that can track and report the location and status of each individual box, pallet, or load. It helps all involved parties better manage packaging and distribution resources.
Smart Packaging has a strong customer empowerment element through great new technological tools. These supply chain tools can offer a customer interface that is used to understand the different purchased products better.
Quality control is another strong advantage of direct distribution and packaging and distribution resource monitoring. Active packages use sensors that are being placed on the product. Organizations can detect the product’s status and see whether it is good or compromised.
Furthermore, advanced packages can even go further by extracting unwanted particles inside the package which can increase the shelf life. These sensors result in easy access to the manufacturer’s final quality products and longer-lasting solutions (impacx, 2020).
Innovative packaging has made the process of locating products much easier and safer, as too many products are difficult to track within a complex supply chain (Choudhury, 2018). It is easy to improve the shopping experience and improve customer services with smart packaging solutions like these.
Make the Most of Packaging and Direct Distribution with ModusLink
The many advantages mentioned above attract companies to switch from traditional packaging to Smart Packaging. It comes down to better packaging and distribution resource management and shifting from manual outdated processes and shifting to processes with advanced technologies. It all comes down to making smart choices with packaging and distribution that make the logistic operation more resilient.
Would you like to know more about the best way to integrate Smart Packaging within your current direct distribution processes and supply lines? Contact one of ModusLink’s industry experts today to get started.
Bibliography:
Aliakbarian. (2019, February 20). Smart packaging: challenges and opportunities in the supply chain. Retrieved from supplychainquaterly.com.
Bianchi. (2017, June 28). 5 Examples of Innovative Uses for RFID Technology in Retail. Retrieved from shopify.com.
BioSpectrum. (2012, July 16). Packing smart for better reach of vaccines. BioSpectrum digital edition. Retrieved from https://www.biospectrumasia.com/.
Cheung, S. &. (2018). Smart Packaging: Opportunities and Challenges. University of Liverpool & University of Northumbria, Department of Mechanical and Construction Engineering & Division of Industrial Design. Liverpool: Elsevier.
Choudhury. (2018, April 05). Top Benefits of Smart Packaging for Packaging Companies | Infiniti Research. Retrieved from Infinity research.
Emprechtinger. (2019, April 18). 5 things you should know about smart packaging. Retrieved from lead-innovation.com.
Fedex. (2020). Tracking Technologies Are the Cornerstone for a Competitive Supply Chain Strategy. Retrieved from Fedex.com.
FreightPOP. (2019, September 3). Barcodes, QR Codes, & RFID In Supply Chain Management. Retrieved from freightpop.com.
Hou, L. &. (2016). The Application of NFC Verification System in Warehouse Management System. South China University of Technology, School of Computer Science and Engineering. Guangzhou,: Atlantis Press .
impacx. (2020). What is smart packaging and its benefits? Retrieved from impacx.io. Jules. (2020, April 8). warehouse automation 101: a complete guide. Retrieved from
easyship.com.
Pagliusi, J. &. (2020). Roadmap for strengthening the vaccine supply chain in emergingcountries: Manufacturers’ perspectives. Elsevier.
Regattieri, S. &. (2013). The Important Role of Packaging in Operations Management. InOperations management .
Richelle. (2021, January 11). Smart packaging. (Boulanger, Interviewer) Thrams. (2020, November 25). Big Benefits of Smart Packaging . Retrieved from
primarypackaging.com.
Vasić, Đ. &. (2018). NFC Technology and Augmented Reality in Smart Packaging. University ofNovi Sad, Faculty of Technical Sciences., Department of Graphic Engineering and
Design. International Circular of Graphic Education and Research.
Ward, h. &. (2019). Rethinking packaging. DHL , Supply chain department. DHL CustomerSolutions & Innovation Represented by Matthias Heutger.
WHO. (2020). Bar-codes, QR codes and Vaccine Vial Monitors in the context of COVID-19 vaccines. World Health Organization.